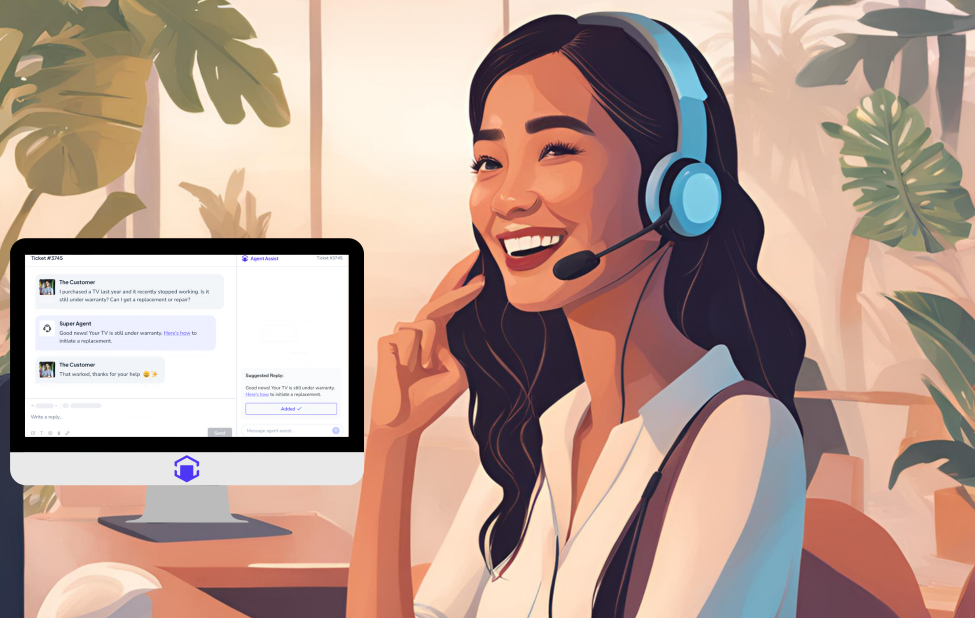
How to Evaluate Enterprise Chatbots
Enterprise chatbots can transform customer and employee experiences. Generative AI chatbots, like Gleen AI, are outstanding at understanding complex questions and generating relevant answers. And, most importantly, Gleen AI doesn't hallucinate.
Enterprise chatbots are transforming customer and employee engagement in the business world. This guide delves deep into enterprise chatbots, highlighting their significance and outlining crucial factors for their evaluation.
Exploring Enterprise Chatbots
Enterprise chatbots represent a significant leap from traditional models. They use AI to have meaningful conversations with their customers and employees.
This helps them build a closer relationship with their audience and provide better support. They have also improved their communication process by making it more efficient.
Enterprise Chatbots: A Game Changer
These AI-driven tools have moved beyond being a fleeting trend. They're pivotal for delivering efficient, continuous customer service, and reshaping how businesses communicate.
Types of Enterprise Chatbots
Enterprise chatbots fall into two categories:
- Customer-Focused Chatbots: These chatbots interact with consumers, providing prompt information and solving issues, thereby elevating customer satisfaction and streamlining customer service processes.
- Employee-Assistance Chatbots: Chatbots are an excellent solution to provide assistance to employees. Tailored to meet an individual enterprise's specific needs, they offer unparalleled efficient, and practical support.
The Differences between a Chatbot and a Generative AI Chatbot
Not all enterprise chatbots are equal.
Enterprise chatbots have existed for more than a decade. Over that decade, we've seen the underlying technology behind chatbots change and evolve. As a result, we've seen chatbots become significantly better over time.
Rule-Based Chatbots
Rule-based bots are the most basic chatbots.
These chatbots operate based on a set of rules, which often create a decision tree for the end user.
A rule-based chatbot behaves much like an interactive voice response (IVR) tree. The bot asks a question, and the user can select from different options. After selecting an option, they can then select from a menu of sub-options, and so on.
Rule-based chatbots only understand specific inputs.
They require more time to set up and maintain.
Most importantly, they cannot understand ambiguous or complex user queries. They're most often used in predictable use cases, like FAQs and basic customer service.
Keyword Matching Chatbots
Keyword matching chatbots look for specific keywords in the user's question.
The chatbot shows a predetermined response when it detects a keyword.
For example:
- Assume a keyword is "password"
- The user asks the question, "I lost my password,"
- The predetermined response might be, "I think you're having a password problem. Here's an article on how to reset your password."
Keyword detection chatbots are extremely simple and can create a bad user experience.
Keyword matching chatbots fail when a keyword is missing from the the question. If the above user asked, "I forget how to access my account," the chatbot would have failed.
Keyword matching chatbots can also fail to detect appropriate context around the keyword. If the user asked, "Can I share my password with a family member?" the chatbot's response would have been inappropriate.
Question Matching Chatbots
A step above keyword matching chatbots are chatbots that recognize user intent to match questions. People often refer to these bots as "conversational chatbots."
They use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the user's intent behind a query. It then matches the user's intent to a predefined set of questions and corresponding answers.
Question-matching chatbots can handle a broader range of queries relative to rule-based and keyword matching chatbots. They can, however, still struggle with complex questions.
In addition, they require a large list of predefined questions and answers. Sometimes, they may also require many different ways of writing the same question.
Generative AI Chatbots
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have enabled a new breed of generative AI chatbots, like ChatGPT.
Generative AI chatbots don't require rules or decision trees. They also don't require large lists of predefined questions and answers.
Generative AI chatbots understand context, can better understand complex queries, and even converse with a personality or style.
Furthermore, generative AI bots can learn from prior user interactions. These bots can become increasingly sophisticated over time, making them highly scalable and versatile.
The Differences between Enterprise Chatbots and ChatGPT
Important differences existing between enterprise chatbots and public chatbots like ChatGPT. These differences include:
- Training Data. Companies tailor enterprise chatbots to their data. Some of their data is public, but much of their data is private. Conversely, ChatGPT trained on public data on the internet.
- Types of Responses: Enterprise chatbots are highly specialized in addressing queries specific to a company's context. They cater to the needs of both employees and customers. ChatGPT provides responses based only on its public training data.
- User Base: Typically, an enterprise's employees and customers use enterprise chatbots. Conversely, anyone can use ChatGPT.
- Purpose: Enterprise chatbots help employees with their jobs or customers solve problems. ChatGPT typically doesn't integrate with specific enterprise systems.
GPTs: Good Enterprise Chatbots?
In November 2023, OpenAI introduced custom GPTs.
GPTs are customized versions of ChatGPT. They allow users to upload private files, integrate with APIs, and share a GPT within their company.
Despite their potential, GPTs face several limitations in an enterprise setting:
- Limited Data Upload. The capacity to upload private data to GPTs is extremely limited.
- Static Knowledge Base. GPTs lack the ability to update their knowledge separately.
- Security Risks. Concerns about hacking and data leakage with GPTs exist.
- Lack of Visibility. OpenAI doesn't offer mechanisms to review the interactions with GPTs.
- Hallucination. Just like ChatGPT, GPTs hallucinate.
Advantages of Enterprise Chatbots
The benefits of deploying enterprise chatbots are multiple:
- Enhanced Satisfaction. Enterprise chatbots deliver faster responses and personalized support, improving the customer experience.
- Always-On Support. Enterprise chatbots provide employee and customer service, 24/7/365.
- Higher Efficiency: They handle routine tasks, freeing up resources.
- Insightful Data Collection: They gather critical customer data for decision-making.
- Adaptable Service Capacity: They easily handle varying customer support needs.
Selecting the Right Enterprise Chatbot
When assessing chatbot platforms for enterprises, consider these criteria:
1. Use of Generative AI. Generative AI helps enterprise chatbots grasp complex series and deliver precise, relevant answers. It also enables real-time language translation, which is ideal for international businesses. You should avoid chatbots lacking generative AI.
2. Custom Data Integration: Top-tier enterprise chatbots utilize your specific company data, not just generic internet data. This significantly enhances response accuracy for your business.
3. Accuracy in Responses: The enterprise chatbot must rely on your company's information, steering clear of fabrications. In other words, it should not hallucinate.
For example, Gleen AI is a leading enterprise chatbot that doesn't hallucinate. We trained Gleen AI and a GPT on the same data. In the video below, the GPT hallucinated, but Gleen AI didn't.
4. Security and Privacy: The enterprise chatbot provider must adhere to SOC 2 Type 2 standards. SOC 2 Type 2 compliance keeps your data safe, confidential, and only used for its intended purposes.
5. Monitoring Capabilities: You need the ability to oversee all chatbot interactions. This includes keeping tabs on both questions asked and responses provided.
6. Adaptive Learning: The enterprise chatbot should regularly improve through feedback, maintaining its effectiveness and relevance.
7. Ease of Maintenance: The enterprise chatbot chatbot must automatically refresh its knowledge, ensuring up-to-date information.
8. Ease of Integration. How simple is it to connect the chatbot with the company's current systems, like help desks, CRM, and order management.
9. Practical Responses: The chatbot should do more than answer questions; it should help users accomplish tasks.
10. Customized Versions. You should be able to clone existing chatbots and create chatbot variations to meet different organizational needs.
11. LLM Agnostic. The chatbot should be compatible with any Large Language Model.
12. Public Cloud Agnostic. The chatbot software can operate on either AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
13. Single Tenancy. To keep your data safe, the chatbot vendor should let you use the chatbot on a dedicated app and database.
14. Dedicated Hosting: You can host the chatbot on a dedicated server to prevent shared resource issues.
15. Private Network Connection. Establishing a Virtual Private Connection between the chatbot and your Virtual Private Cloud guarantees secure data exchange.
16. Scale: The chatbot should efficiently manage growing interaction volumes as your business expands.
17. Service Availability Guarantees: The provider should offer a defined level of uptime.
18. Customer Service Commitments: Specific customer service response times agreements are essential.
Conclusion
Enterprise chatbots – especially generative AI chatbots -- stand at the forefront of business innovation.
Gleen AI exemplifies this, particularly with its unique no-hallucination feature.
Get a demo of Gleen AI, or create a free generative AI chatbot using Gleen AI now.



